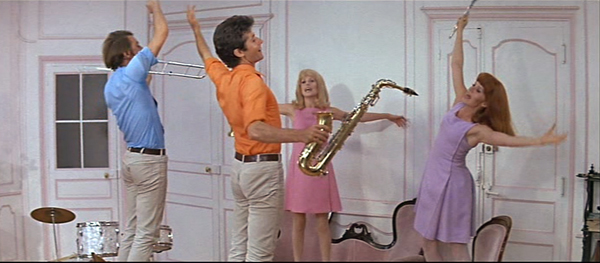How LA LA LAND is made
Monday | January 23, 2017 open printable version
open printable version
La La Land (2016).
The formal method is fundamentally simple. It’s the return to craft (masterstvo).
Viktor Shkovsky, 1923
DB here:
Not how it was made. We’ll get “The Making of La La Land” as a DVD bonus, and there are already behind-the-scenes promos.
No, this is about how it is made.
On this site, we mostly practice a criticism of enthusiasm. We write about what we like, or at least about films that intrigue us from the standpoint of history or aesthetics. Sometimes, what interests us intersects with a current controversy. Take La La Land.
Some of my cinephile friends disapprove of it. It swipes too much, they say, from classic studio musicals and the work of Demy, and it doesn’t live up to either model. But tastes change. I remember when the classic musicals that we venerate were considered fluff, and I recall how Demy’s films, especially Les Demoiselles de Rochefort, were held at arm’s length by many of my 60s pals. “He tries too hard,” a friend remarked. Some say that about Chazelle, and perhaps in a few decades La La Land will be remembered fondly.
In any case, I’m not aiming to denounce this ambitious, agreeable film. I’m more interested in asking how La La Land accords with the craft of studio musicals and Demy’s efforts. I’m also interested in tracing its affinity with a third tradition of song-and-dance: the Broadway show.
Along all three dimensions, I hope to take Shklovsky’s advice and ask about craft. La La Land is both derivative and original. Actually, most movies are, though in various proportions.
The song plot
If we want to understand how film form and style work, we can’t neglect the nuts and bolts of moviemaking. In trying to achieve particular effects, filmmakers have created craft traditions, favored options bounded by loose limits. Mostly these traditions grow up intuitively, as solutions that just feel right. In any case, behind the cluster of preferred practices we can often find principles of design and execution that can be made explicit.
A lot of what Kristin and I have been doing since the 1970s consists of trying to bring to the surface filmmakers’ underlying habits and conventions. Those help shape how viewers respond to films. We aren’t maniacs for systematization—art can’t be utterly systematized—but as analysts we want to discern patterns of story and style, what earlier entries have called schemas. And as historians we want to understand how patterns of story and style get passed down from earlier films, and passed around among contemporaries.
For example, some narrative schemas of American studio cinema are what I aim to lay bare in Reinventing Hollywood: How 1940s Filmmakers Changed Movie Storytelling. Without invoking the big guns of theory, I try to point out how craft traditions of plotting and narration got recast in those crucial years. A recent entry hereabouts tries to show the legacy of those years surfacing in current releases, La La Land included.
 Other researchers work along these lines, and not just in film. Art historians have been doing this sort of research for a long time, as have musicologists. A more recent example in the domain of theatre aesthetics is Jack Viertel’s exhilarating book The Secret Life of the American Musical. Its subtitle, How Broadway Shows Are Built, is a throwback (inadvertent, I suppose) to Shklovsky’s essay “How Don Quixote Is Made.” The impulse is the same: to x-ray an art work, to reveal some fundamental principles of construction, while also doing justice to its revisions of inherited traditions.
Other researchers work along these lines, and not just in film. Art historians have been doing this sort of research for a long time, as have musicologists. A more recent example in the domain of theatre aesthetics is Jack Viertel’s exhilarating book The Secret Life of the American Musical. Its subtitle, How Broadway Shows Are Built, is a throwback (inadvertent, I suppose) to Shklovsky’s essay “How Don Quixote Is Made.” The impulse is the same: to x-ray an art work, to reveal some fundamental principles of construction, while also doing justice to its revisions of inherited traditions.
What Viertel brings to the table is the “song plot,” a sequence of musical numbers that has become conventional in Broadway shows. Often, of course, many numbers enhance the dramatic action, but sometimes they’re inserted for a change of mood or a burst of energy. The song plot both echoes the action plot and provides its own arc of pleasure, with musical numbers that may be more or less extraneous to the main action.
What makes Viertel’s anatomy of shows interesting is that even the narratively “irrelevant” numbers tend to occur in the same spot from show to show, and they have a common emotional quality. They aren’t just “spectacle interrupting narrative,” to use a film-studies commonplace. As spectacle, they have their own pattern, and that’s gratifying alongside the pleasures of the story. Viertel’s macro-schema is probably known to many insiders and fans, but it was all news to me, and it helps me understand the musical spine of this recent movie.
Hence today’s title, of an entry that is 100% spoiler-filled. I’ll consider La La Land as a classically constructed film. Then I’ll test its “making” against Viertel’s template of a musical. I conclude with some remarks on how analyzing these patterns highlights the movie’s variance from adjacent traditions.
From meet-cute to remeet, and re-remeet
Start with the Hollywood plot structure. Kristin has argued that even though mainstream American screenwriters sometimes claim to be following a three-act plot model, their craft practice often pushes them to a four-part schema. (She has discussed this here, and I’ve given examples here and here.) Specifically, the long second “act” is usefully thought of as two separate parts split by the film’s midpoint.
The conventional plot pattern consists of a Setup in which protagonists define their goals; a Complicating Action that redefines those goals; a Development that muddles, delays, or intensifies the goals; and a Climax that resolves them. These parts typically run 20-30 minutes, and films of varying lengths, long or short, can include more or fewer parts than these four. In most cases there will also be an epilogue or “tag.”
La La Land runs almost exactly 120 minutes, not counting the opening logos or the end credits. The Setup (running 25 minutes) establishes Mia and Sebastian as dual protagonists, caught in the midst of the initial traffic jam.
We then follow Mia through her day as a barista, her failed audition, her return to her apartment, and her agreement to go out to a networking party with her flatmates.
A flashback returns us to the traffic jam, and now we follow Sebastian to his apartment, where in a parallel to Mia’s day he makes coffee, rummages through unpaid bills, and talks with his sister. He goes on to his job as pianist playing Christmas music at a cocktail bar. Mia, who’s come in by accident, stands before him, moved by his switch into improvised jazz. But Sebastian is fired, and disgruntled, he coldly bumps past her.
The Complicating Action starts after Mia fails another audition. She goes to a pool party and sees Sebastian in the ensemble. She teases him, and they leave the party together. Although there’s friction between them, they start a friendship. They confess their dreams: she wants to be an actress and he wants to start a club that hosts classic jazz.
Mia absentmindedly agrees to go to a movie with him on a night she has a date with her boyfriend. But she’s haunted by Sebastian’s music and she finds him at the theatre, watching Rebel without a Cause. They go to the planetarium featured in the film and kiss. At the end of the Complicating Action, about 60 minutes in, Mia resolves to write a one-woman show for herself.
The Development is the stretch where backstory is introduced, obstacles create delays, and subplots intertwine with the main action. Since in La La Land the romance seems solid (there are no love rivals), and there are no secondary characters of consequence, the film is devoted to the other major plotline: the obstacles encountered in our couple’s quest for success. Those in turn affect the romance.
A Development also typically relies on montage sequences, and we get plenty here. Mia works on her show, while Sebastian is offered a chance to join his friend Keith’s combo. To stabilize his life with Mia, he takes the job.
Soon he’s on tour, and the band finds some success, though he’s compromising his principles. “Do you like the music you play?” Mia demands, and he evades answering. The crisis comes when a photo shoot delays his arrival at her premiere, which is a fiasco.
Mia declares: “It’s over”—meaning both her career and their affair. She goes back home. We’re at the 90-minute mark.
We’re ready for the Climax, which is often driven by a deadline. Sebastian takes the call asking Mia to audition, and he rushes her back to it. She gets the part, and the two of them decide to wait and see how their relationship develops.
Five years later, Mia is now a success. This seems an abrupt, even anti-climactic turn of events, coming only eleven minutes after the Climax started. Apparently, despite their declarations of undying love, the couple’s romance was never rekindled. We see Mia visit the café where she was once a barista and return to her hotel and her husband and daughter. Her activities are crosscut with glimpses of Sebastian alone in his apartment. In effect, this passage balances our alternating introduction to the couple during the Setup.
Mia and her husband drop in on a club that turns out to be Sebastian’s. Mia and Sebastian eye each other longingly. Mia watches him play Their Song, and this launches an apparently shared fantasy of an alternate-world climax and resolution.
There’s a replay of the two of them at the cocktail bar, but this time Sebastian doesn’t brush past her. They kiss passionately. After this what-if premise, the race to the audition is replayed in stylized form, and the trajectory of Mia’s career—going to Paris, finding screen success, forming a family—is reenacted with Sebastian as her mate. At the end, Sebastian, not her husband, is sitting with her in the club (listening in effect to himself), and they kiss.
This soufflé of flashbacks and fantasies ends the plot on the conventional romantic clinch. But the film’s tag, of course, is their return to reality and the sad smiles shared as she goes off with her husband. In all, this double climax/ resolution turns out to run almost thirty minutes, which would be unusually long for a non-musical.
As is customary in Hollywood narrative, motifs and parallels crisscross the film. The opening song on the freeway lays out hints of what is to come. The sequence alternates a woman singing about a career as a film star (“It called me to be on that screen”) and a man singing about a career honoring old music (“ballads in the bar rooms left by those who came before”). Anticipating the finale, the woman’s song includes mention of a boy seeing her on the screen and remembering that he knew her.
More parallels and rhymes follow. Mia nearly stands up Sebastian on their date; he misses her show. Each encourages the other to keep struggling. Mia’s blockhead boyfriend anticipates her eventual GQ husband, as if she has decided not to go for the edgy type Sebastian is. The motif of Mia’s beloved aunt, who inspired her love of movies and her urge to act, gets dramatized twice, once in her one-woman show and more successfully in her audition song, “Here’s to the Ones Who Dream,” which wins Mia the movie part.
So many things are doubled that it’s not surprising that the Setup parallels each protagonist’s day and establishes the crucial moment at the supper club. That too gets replayed—once in the real world, as she and her husband hear Sebastian’s performance of his tune for her, and once at the start of the fantasy projection of their future, which becomes a replay of her actual life with her husband.
So far, so classical. But—duh, as they say–La La Land is also a musical.
That’s the Broadway melodies
My outline of La La Land‘s construction is fairly hollow, and could be filled in with closer consideration of the moment-by-moment process of conflict and change, or the flow of information as we’re attached to one character or the other. But we get access to another layer of “making” by considering the film as a musical–more specifically, a Broadway musical. (No surprise that the lyricists are stage-based.) Viertel is a big help here. His account of the prototypical song plot fits La La Land fairly well, and the places where it doesn’t are pretty interesting too.
Broadway shows of the Golden Age (roughly 1942-1975) tend to have the double plotline characteristic of Hollywood films. Both shows and movies make romance central, and this permits the action plot and the song plot to fit together. In Broadway shows, as in many films, paired protagonists try to find happiness in both love and work. Intertwined goals are central to getting the action moving, and so goals are ingredient to the song plot.
Director Damien Chazelle apparently hesitated about opening with the freeway-gridlock number, but he and editor Tom Cross decided to announce the film’s song-and-dance premises immediately. I think the pressure of show-biz tradition helped. According to Viertel, the prototypical musical might start with a solo, as with Oklahoma!’s “Oh, What a Beautiful Mornin’.” But it may also start with a “blowout,” and La La Land’s “Another Day of Sun” surely counts as that. It establishes milieu and mood, in somewhat the manner of the bouncy introduction to Damon Runyon’s world in Guys and Dolls, and it announces the central goal of showbiz success.
Viertel marks the next number as crucial. It’s the “I Want” song, the initial crystallizing of the protagonist’s goals. In La La Land, that position is occupied by “Someone in the Crowd,” which starts as an ensemble number with Mia’s brassy roommates but devolves into a solo for her. By then, the “someone” she seeks isn’t only a career-enhancing meetup but a love partner.
After the plot moves into the Complicating Action phase, Mia and Sebastian meet cute again at the pool party. He’s playing in a lame retro band and she teases him, in revenge for his brushoff at the piano bar. There follows the next key item in the song plot, what Viertel calls “the conditional love song.” The prototype is “If I Loved You” (Carousel). Essentially it declares how wrong the boy and girl are for each other. It has the function of blocking and deferring the goals of the love plotline, and in non-musical rom-coms, it takes the shape of verbal sparring, quarrels, and competition (as in, say, You’ve Got Mail).
Clearly, “A Lovely Night” is a conditional love song, as Mia and Sebastian remark on how the LA view would be perfect for a couple who were really in love. But as often happens, while the words refuse romance, the music and the choreography show that the two ought to be together.
At this point in the song plot, Viertel suggests, the show needs a burst of energy. In La La Land, what he calls The Noise is delivered by the instrumental number at the jazz club, called in the soundtrack album “Herman’s Habit.” It’s not narratively gratuitous, as it’s an AV demo of the sweet collective creativity Sebastian admires in classic jazz. The number also marks Mia’s growing affection for Sebastian and her belief in his dream.
But now Viertel’s Broadway template diverges from La La Land, and it points up a crucial factor in the film. The conventional song plot typically devotes a number to a second couple or a subplot. Think of the comic couple in The Pajama Game, and the number “I’ll Never Be Jealous Again,” which expresses Hines’s unreasonable fear of losing Gladys. That show also includes the subplot of labor negotiations with the devious Mr. Hasler. But La La Land doesn’t have a subplot involving a second couple, a romantic triangle, or a villain. So no such song appears.
Next on the Viertel template is a star turn, a distinctive number for one of the major players. That function is fulfilled by “City of Stars,” the introspective musing of Sebastian on the pier. Viertel indicates that the following number tends to be a high-energy tentpole that starts the buildup to the first-act curtain. That position is occupied by the airy pas de deux at the Griffith Observatory on their first date.
We’re now into the Development section, with Mia working on her one-woman show and Sebastian touring with his friend’s combo. The summer montage sequences offer other numbers, including Sebastian’s performance with the jazz group and the “City of Stars” duet with the couple at the piano. These bits don’t fit easily into Veirtel’s template, but what does is the “curtain song,” the Messengers’ “Start a Fire” number. It’s splashily performed at the concert that makes Mia apprehensive.
The performance functions as a curtain song, I think, because of Viertel’s claim that the close of the first act typically signals dashed hopes. The curtain numbers of Gypsy, Guys and Dolls, Carousel, West Side Story, and other shows announce a failure to achieve goals. “The most typical kind of first act curtain,” Viertel explains, is “the unraveling, in an instant, of everything everyone has planned.” It’s too strong a description of La La Land’s concert, but Sebastian’s cynical keyboard tweaks during the band’s blast of adult contemporary R&B mark him as a sellout. “Do you like the music you play?” He seems to have given up his dream, a failure that becomes the first crack in the couple’s relationship.
There are fewer discrete numbers in the film’s last stretch; it lacks several songs in the Viertel template (the Welcome-Back number, the second star turn, more subplot songs, and the first big showpiece). Owen Glieberman has noted that the film’s second hour is notably less buoyant, and the first full-blown number in the Climax is melancholic.
“The Fools Who Dream” is gently confessional, in contrast to the overheated delivery of Mia’s earlier auditions. It’s what Viertel calls a second-act showpiece, and true to that convention it yields a big plot point: She wins the role.
The resolution of the plot, what Viertel calls the “next-to-last scene,” need not be a number at all. It’s often a “book scene,” and so it is here. After Mia wins the role, she and Sebastian admit both their love and the difficulty of staying together.
There follows the finale, a bookend to the freeway opening. “The 11:00 scene,” as Viertel points out, is often a wide-ranging reprise. La La Land’s eight-minute sequence presents a synthesis of the musical motifs and a revised, stylized version of Mia’s career.
Oklahoma! is usually credited with popularizing the fantasy ballet interlude, a convention that was picked up in the “Miss Turnstiles” daydream of On the Town, the Girl Hunt of The Band Wagon, and many other what-if sequences in Hollywood musicals. As a stroke of novelty, La La Land saves its fantasy ballet for the end, and makes it a bittersweet contrast to the real resolution.
Reports on the creative process behind La La Land indicate that the filmmakers were constantly weighing their choices about where to put their musical interludes. The fact that they settled on a layout that sticks fairly closely to the Broadway template suggests that Viertel’s song plot has advantages that creators intuitively gravitate towards. Its emotional arc both complements and extends the drama-driven plot.
The long and the short of it
Viertel’s anatomy of the Broadway song plot nicely fills out some patches of classical dramaturgy. It helps us better understand the tacit guidelines that creators follow, and it shows how even movies not drawn from stage shows have absorbed some of their conventions. Yet Viertel’s layout does more than point up the affinities between La La Land and stage musicals. It also helps us see where the film rejects the traditional schema.
The film’s deletions from the song plot omit love triangles (of any consequence), subplots, villains, and parallel couples. Sebastian’s sister is basically an expositional device, while Mia’s roommates are barely characterized and her parents barely seen. The bandleader Keith is mostly a mouthpiece for a musical idiom, and the other members of the combo aren’t individualized. No secondary character is granted a show-stopper like “Sit Down, You’re Rocking the Boat” or “Steam Heat” or “Make ‘Em Laugh.”
In sacrificing subplots and side bits, La La Land forfeits what such devices add: a different range of emotions, thematic contrasts, relief from overexposure of the two lovers, and comic relief. The film gives up accessory pleasures, like the counterpoint romance of Nathan Detroit and Adelaide in Guys and Dolls, or the ballad of the parents at the piano in Meet Me in St. Louis. In a bold genre change, La La Land stands or falls by its two principals.
Strangely, this spare plot consumes two full hours. Compare its Hollywood counterparts. Cover Girl, another showbiz tale, runs fifteen minutes shorter, but has time for a fully-rendered sidekick, a competitor for the heroine Rusty, a nice role for Eve Arden, and a parallel plot (thanks to flashbacks) devoted to Rusty’s grandmother. At 95 minutes, On the Town squeezes in three couples and a New York travelogue. As for the often-invoked Demy, compare the 90-minute Umbrellas of Cherbourg, which manages to deck the plot out with two old ladies and two deftly characterized rivals for the central couple. Better yet, recall Les Demoiselles de Rochefort. Granted, it too runs two hours, but it has to pack in five couples, one triangle, a starstruck café waitress, and for good measure a serial killer.
More broadly, La La Land doesn’t give its protagonists sharply defined goals. They just want to succeed, through rounds of auditions or short-term music gigs. In Cover Girl Rusty is given clear-cut options: To sign on as a model or stay a club dancer? To marry a piano player or a Broadway impresario? And as Viertel points out, there’s often a bigger issue at play—statehood in Oklahoma!, modernizing a country in The King and I, moving a family from St. Louis to New York. Nothing like this hovers over the couple in this rather hermetic movie.
What fills up that extra running time in La La Land? For one thing, the very parallels that I’ve mentioned, notably the extended scenes in the café; but also, I think, the pool party, with its sideswipes at the movie industry, and the planetarium dance, pretty as it is. A older studio-era film would have gotten the romance going sooner, in the Setup, sharpened the choices facing the characters, and fleshed out their milieu with friends, family, and minor players who get a little bit of the spotlight. (Keith would almost certainly have gained a romantic partner, hopefully a wise-cracker.) A Demy film would have added more characters as well, with a crisp geometry of counterparts and substitutions. Everything would be color-coded too.
The slimness of the plot can be taken as a point against the film, but focusing a musical so tightly on the couple was probably worth trying. If anybody cares, I enjoyed the film, and—to invoke the distinction between taste and judgment—I think it’s a solid, sometimes stirring effort. But what matters to me now is the way that thinking about craft traditions, particularly as they affect structure, allows us to plot some ways in which La La Land is both traditional and original. Evaluation is important, but it can be guided by analysis. An essential part of criticism involves studying how things are made.
Thanks to Jeff Smith for advice about the Messengers’ musical idiom, and to Michael Campi and Peter Rist for discussions about the film.
The quotation from Shklovsky at the start comes from the extract from A Sentimental Journey (1923) in Viktor Shklovsky: A Reader, ed. and trans. Alexandra Berlina (Bloomsbury, 2017), 150. For another Shklovskyan foray into contemporary moviemaking, you can try “Pulverizing Plots.” My quotation from Viertel on first-act curtains comes from The Secret Life of the American Musical, p. 152.
More on the making: A fairly detailed account of LLL‘s choreography is provided at the Verge, with more film references than you can shake a stick at. On the authenticity dimension, Glenn Kenny gets on the case of jazz purists.
Kristin’s discussion of four-part structure is at its fullest in Storytelling in the New Hollywood: Analyzing Classic Narrative Structure. I discuss it and apply it to some examples in The Way Hollywood Tells It: Story and Style in Msodern Movies. For more examples, visit our category Narrative Strategies.
P.S. 24 January 2017: LLL has garnered a heap of Oscar nominations this morning. Now this Los Angeles Times story supplies more information on how it was made (financially).
Les Demoiselles de Rochefort (1967).